The Ross Sea MPA was established in October 2016 by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR). This international commission is made up of 26 members and 10 other countries that have adhered to the Convention, including France. One of its objectives is to create a network of marine protected areas in Antarctica.

Why is the Ross Sea important?
The Ross Sea is one of the last remaining stretches of ocean on Earth that has not been harmed by human activity. It is yet to be damaged extensively by overfishing, pollution or invasive species. In addition to being one of the most abundant areas in the world for species of all kinds, it has offered scientists the opportunity to study its biodiversity for years.
Why is Ross sea MPAs so effective?
With its 2.09 million square kilometers, the Ross Sea MPA around Antarctica is the largest in the world. Within it, 1.66 million square kilometers, or nearly 80%, are a « strong protection » zone where no commercial fishing is allowed. For the rest, only vessels with a CCAMLR permit can fish.
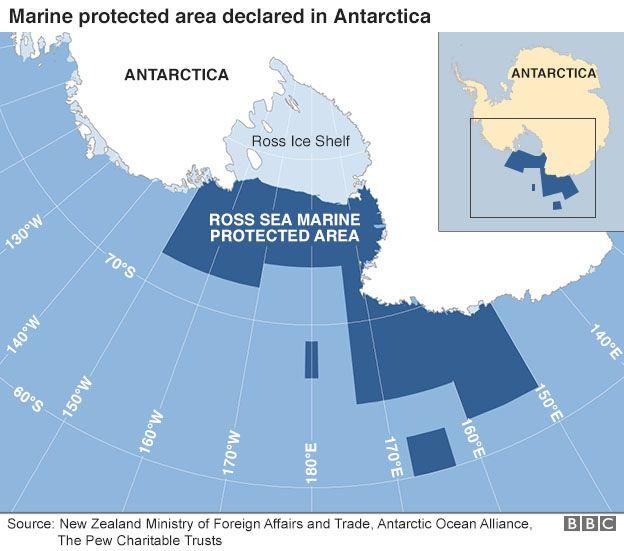
« The United States helped organize baseline data studies for the MPA in 2018 as a starting point. Since then, current research and monitoring projects focused on the Ross Sea are extensive, » the Pew Trust explains. Many member states are conducting research and monitoring relevant to the Ross Sea region MPA. « Based on this research and monitoring, the Ross Sea Region MPA is continually reviewed to assess whether it is meeting its conservation goals. » These numerous studies and dozens of annual meetings organized by CCAMLR allow this area to be considered by scientists as the most protected in the world.
Moreover, in order to ensure its protection, many countries such as New Zealand, Italy and South Korea send maritime surveillance patrols in its heart.

